
.
How phytochemicals help gut health
Phytochemicals, particularly the polyphenol group, give food its colour, taste and aroma but have enormous health benefits via their ability to reduce excess inflammation and improve oxidative efficiency. An increasing body of evidence is now revealing their vital role in improving the microbiome [Kol, Davinilli, Peron]… read more about the different types of phytochemicals
Phytochemicals such as plant lignans found in beans and nuts, ellagitannin found in pomegranate and curcumin found in turmeric act as prebiotics which support the growth of healthy bacteria [Carlson, Arcanjo, Alves-Santos]. Citrus Sinensis rich in bioflavonoids and chamomile rich in Apigenin both directly reduce gut inflammation creating a more favourable growing environment for the health bacteria [Sirvastava, Matic]. Resveratrol found in grapes and polygonum cuspidatum root, enhances the formation of a protective biofilm over healthy bacteria such as Lactobacillus, facilitating healthy colony formation [Al Azzaz]. The properties of these foods is why they were chosen for the Phyto-v supplement to be taken along side the Yourgutplus+ probiotic in the latest covid-19 study
.
Why gut health health is so important
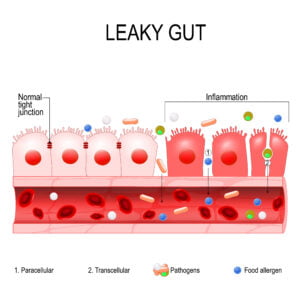
Gut consequences poor gut bacterial growth:
- Food poisoning including Helicobacteria
- Food intolerance
- Food allergies
- Stomach and duodenal ulcers
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Bowel cancer
- More bowel symptoms after covid
- More chance of long covid
Whole body consequences of a leaky gut:
- Fatigue, low mood, depression
- Reduced sports performance
- More colds and flu
- Increase risk after catching covid
- Higher risk of long covid
- Arthritis, Osteoporosis
- Eczema and atopic skin conditions
- Diabetes, high cholesterol, heart disease
- Dementia and Parkinson’s disease
- Premature ageing
.
How to improve phytochemical intake

Phytochemical rich supplements, if well made, are a convenient way to increase intake and spread intake across the day. They can also contain foods which are not commonly available or not commonly used in Western diets. Most have not been evaluated in robust medical trials. The notable exception is Phyto-V which was so beneficial in the two recent studies involving men and women suffering from symptoms of covid-19 .. see more
It’s important to combine phytochemical rich foods with bacteria rich foods. Probiotics help the breakdown of polyphenols into more readily absorbed and more bioactive varieties [Morrison]. So as well as bacteria rich foods a good quality probiotic supplement would be advantageous
References
Carlson JL, Erickson JM, Lloyd BB, Slavin JL (2018) Health Effects and Sources of Prebiotic Dietary Fiber. Curr Dev Nutr 2: nzy005.
Alves-Santos AM, Sugizaki CSA, Lima GC, Naves MMV. Prebiotic effect of dietary polyphenols: A systematic review. Journal of Functional Foods. 2020; 74 (1): 1-34. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464620303935.
Al Azzaz J, et al. Resveratrol Favors Adhesion and Biofilm Formation of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei Strain ATCC334. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21 (15): 5423-5446. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7432909/.
Morrison D et al. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes. 2016; 7 (3): 189. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4939913/
Koh A, et al. From dietary fibre to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell. 2016; 165 (6): 1332-1345. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S009286741630592X.
Arcanjo N et al. Resveratrol protects Lactobacillus reuteri against H2O2- induced oxidative stress and stimulates antioxidant defenses through upregulation of the dhaT gene. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2019; 135 (1): 38 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0891584918321646.
Gross G, et al. In vitro bioconversion of polyphenols from black tea and red wine/grape juice by human intestinal microbiota displays strong inter-individual variability. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2010; 58 (18): 10236-10246. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jf101475m.
Matić I,Savikin K, Zdunic G et Chamomile and Marigold Tea: Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of Anticancer Activity Phytotherapy Research Volume 27 (6), 852-58 https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.4807





[…] producing) bacteria. To date the most significant evidence for the use of probiotics and phytochemical rich food supplements come from the UK phyto-v study. They tested two supplements Yourgutplus+ and phyto-v in a large […]
[…] Why phytochemical aslo improve gut health […]
[…] by whole organic ginger which makes it much more palatable. Ginger is rich in bio-enhancing natural phytochemicals which helps with iodine absorption and optimal use in the body. Ginger also has numerous other […]